
No one will drive us from the paradise which Equi7Grid created for us
GitHub: https://github.com/csaybar/equi7grid-lite 🌐
PyPI: https://pypi.org/project/equi7grid-lite/ 🛠️
Overview 📊
The equi7grid-lite package implements a user-friendly Python interface to interact with the Equi7Grid grid system. With this package, users can convert geographic coordinates to Equi7Grid tiles and vice versa.
equi7grid-lite is an unofficial Python implementation of Equi7Grid. It offers improvements and a simplified interface for grid interaction. This implementation differs from the official version in three key ways:
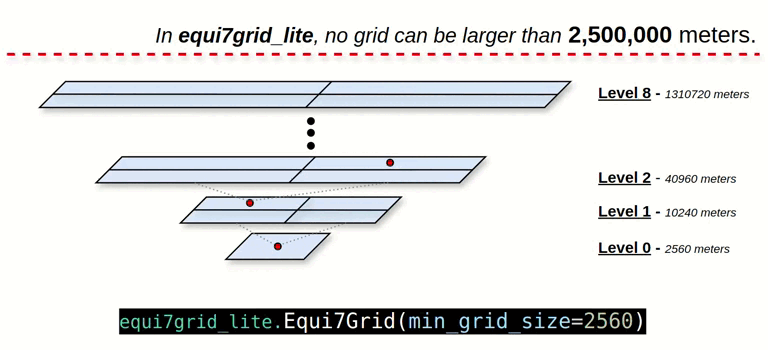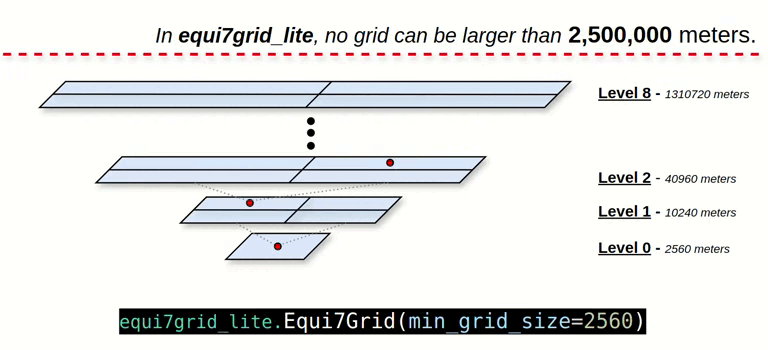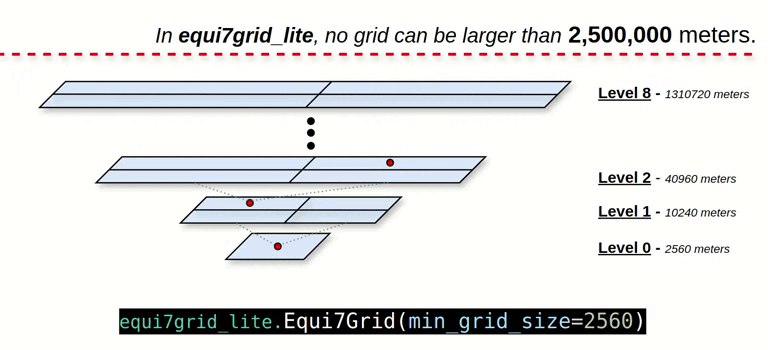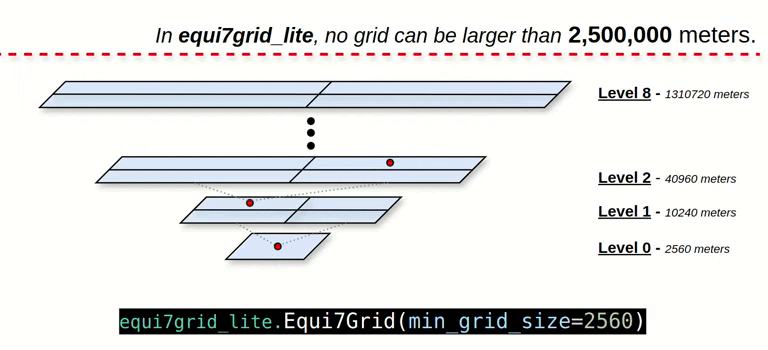
- Quad-Tree Grid Splitting: Users split the grid in a Quad-Tree fashion, with each grid level divided into four tiles.
- Revised Grid ID Encoding: The grid ID is encoded in meters, without the "T1", "T3", or "T6" tile system references.
- Upper Bound Level: The grid level is capped at a threshold of 2,500,000 meters to manage grid complexity.
Key Features ✨
- Coordinate Conversion: Convert between geographic coordinates and Equi7Grid tiles easily. 🌍
- Quad-Tree Grid Management: Supports splitting and managing grids in a Quad-Tree structure. 🗺️
- Cubo Integration: Use equi7grid-lite in combination with Cubo for Earth Observation (EO) data retrieval. 🛰️
Please refer to the Equi7Grid repository for more information on the official implementation.
Installation ⚙️
Install the latest version from PyPI:
pip install equi7grid-lite
How to use 🛠️
Basic Usage: Working with the Equi7Grid 🗺️
Convert geographic coordinates to Equi7Grid tiles
from equi7grid_lite import Equi7Grid
grid_system = Equi7Grid(min_grid_size=2560)
lon, lat = -79.5, -5.49
grid_system.lonlat2grid(lon=lon, lat=lat)
# Equi7Grid(min_grid_size=2560)
# ----------------
# levels: 0, 1, ... , 7, 8
# zones: AN, NA, OC, SA, AF, EU, AS
# min_grid_size: 2560 meters
# max_grid_size: 1310720 meters
Convert from grid ID to geographic coordinates
grid_system.grid2lonlat(grid_id="SA2560_E2009N2525")
# id lon lat x y zone level land geometry
#0 SA2560_E2009N2525 -79.507568 -5.485739 5144320.0 6465280.0 SA Z0 True POLYGON ((514560...
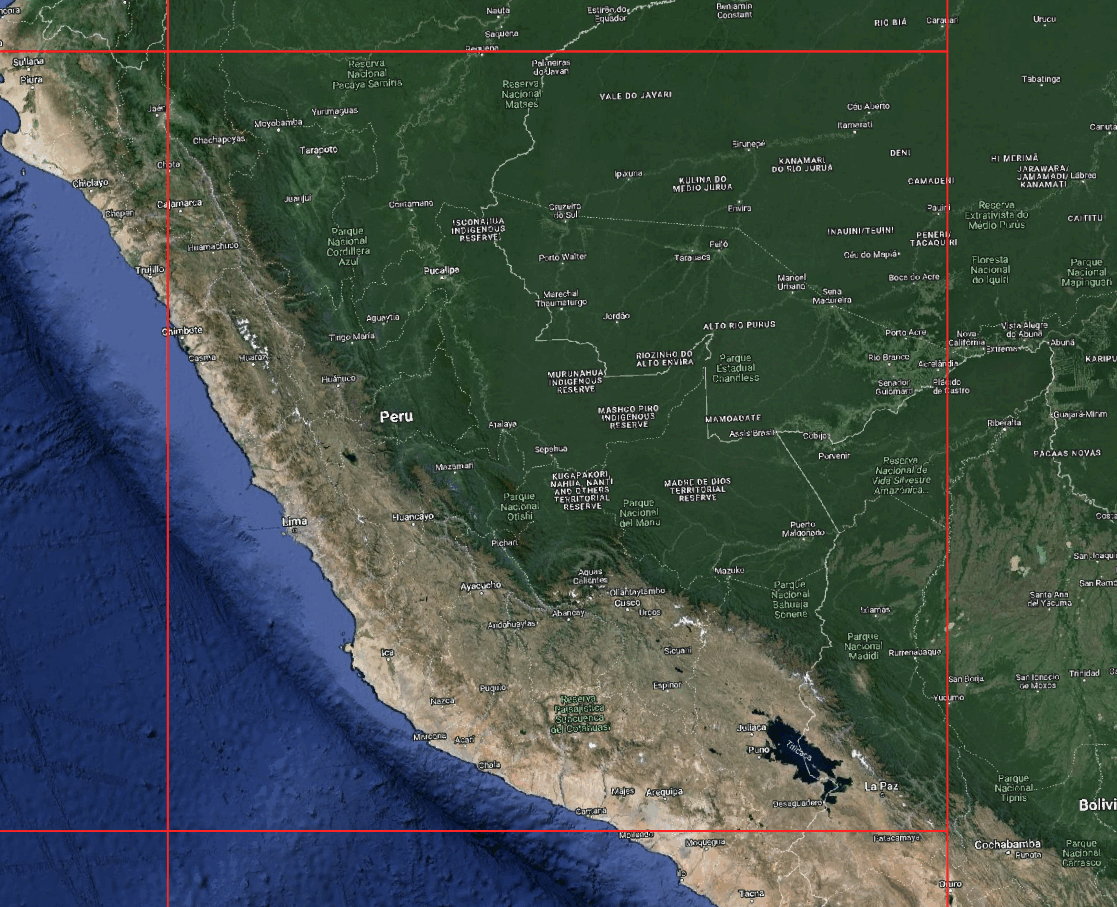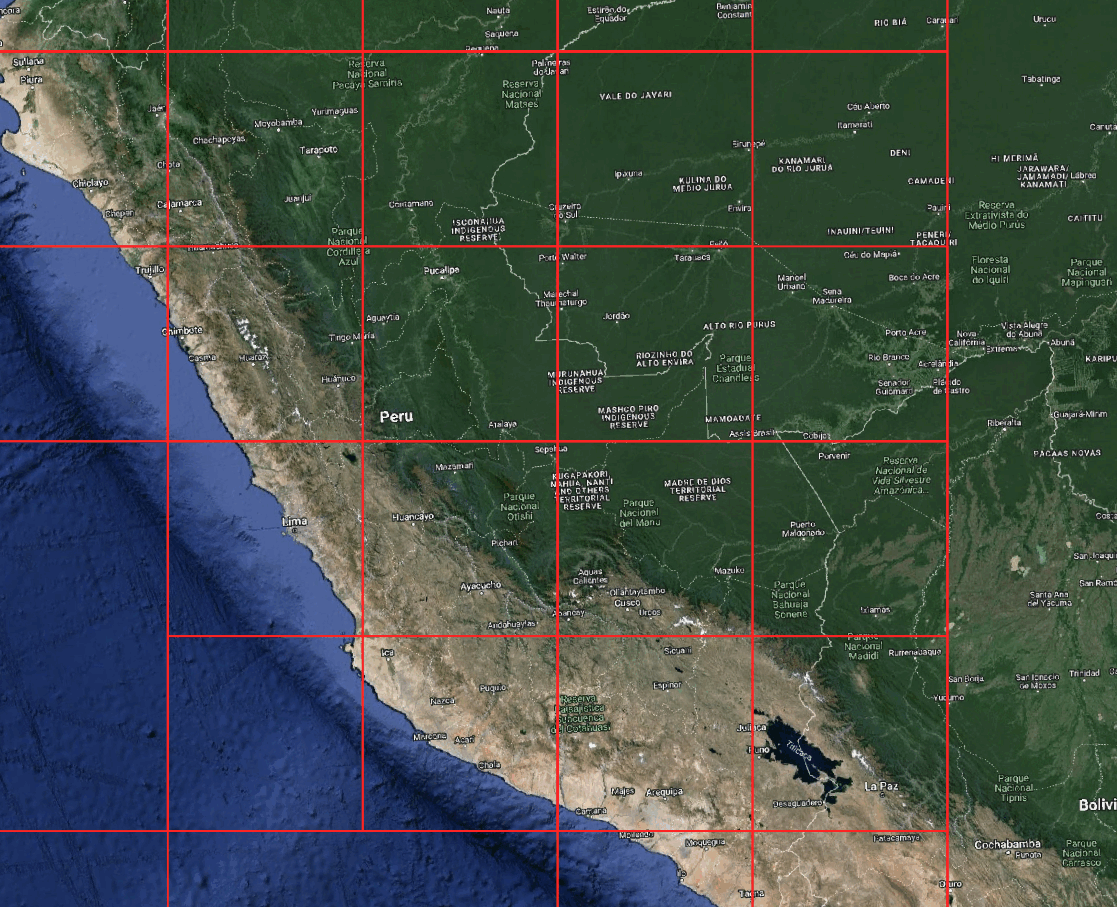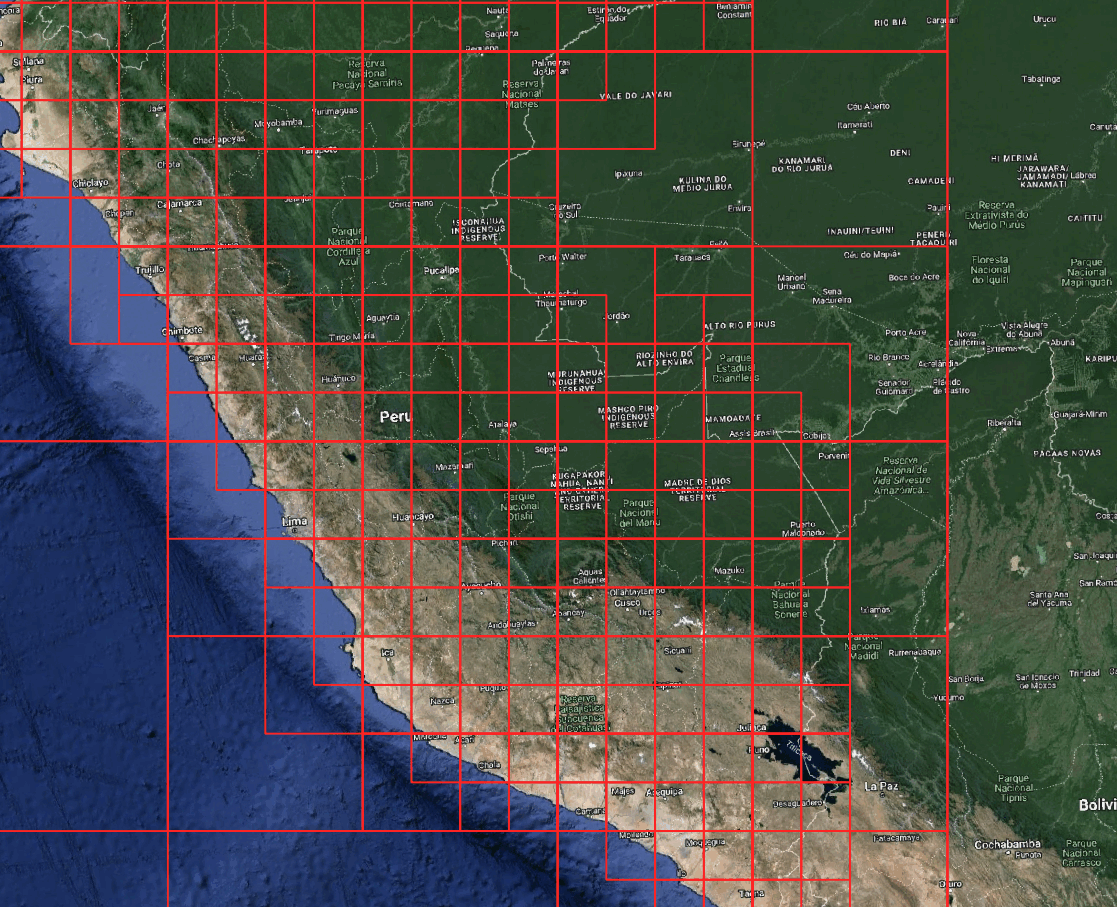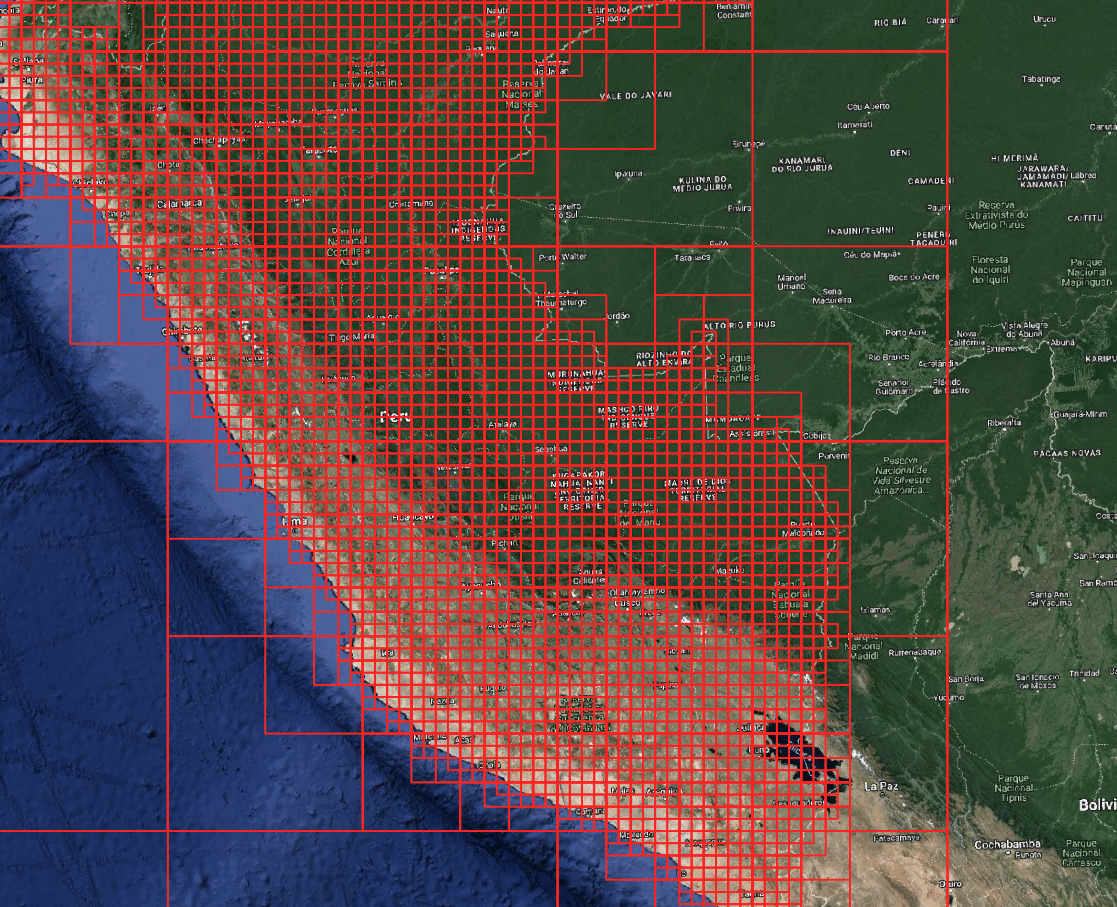
Grid Management: Creating Grids for a Specific Region
You can create a grid for a given bounding box or polygon.
import geopandas as gpd
from equi7grid_lite import Equi7Grid
# Load country geometry (e.g., Peru)
world_filepath = gpd.datasets.get_path('naturalearth_lowres')
world = gpd.read_file(world_filepath)
country = world[world.name == "Peru"].geometry
# Create a grid of Equi7Grid tiles that cover the bounding box of the country
grid = grid_system.create_grid(
level=4,
zone="SA",
mask=country # Only include tiles that intersect the polygon
)
# Export the grid to a GeoDataFrame
grid.to_file("grid.shp")
Cubo Integration 🛰️
Use the equi7grid-lite package with cubo to retrieve EO data.
import cubo
import rioxarray
from equi7grid_lite import Equi7Grid
from rasterio.enums import Resampling
# Initialize Equi7Grid system
grid_system = Equi7Grid(min_grid_size=2560)
# Use CUBO to retrieve EO data
lon, lat = -122.4194, 37.7749
cubo_params = grid_system.cubo_utm_parameters(lon=lon, lat=lat)
da = cubo.create(
lat=cubo_params["lat"],
lon=cubo_params["lon"],
collection="sentinel-2-l2a",
bands=["B04", "B03", "B02"],
start_date="2021-08-01",
end_date="2021-10-30",
edge_size=cubo_params["distance"] // 10,
resolution=10,
query={"eo:cloud_cover": {"lt": 50}}
)
# Reproject and resample the cube
image_reprojected = da.to_dataset("band").rio.reproject(
cubo_params["crs"],
resolution=2.5,
resampling=Resampling.lanczos
)
License 📝
This package is released under the MIT License. For more information, see the LICENSE file.
Contributing 🤝
Contributions are welcome! For bug reports or feature requests, please open an issue on GitHub. For contributions, please submit a pull request with a detailed description of the changes.
Citation 📄
If you use this package in your research, please consider citing the original Equi7Grid package and paper.
Package:
@software{bernhard_bm_2023_8252376,
author = {Bernhard BM and
Sebastian Hahn and
actions-user and
cnavacch and
Manuel Schmitzer and
shochsto and
Senmao Cao},
title = {TUW-GEO/Equi7Grid: v0.2.4},
month = aug,
year = 2023,
publisher = {Zenodo},
version = {v0.2.4},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.8252376},
url = {https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8252376}
}
Paper:
@article{BAUERMARSCHALLINGER201484,
title = {Optimisation of global grids for high-resolution remote sensing data},
journal = {Computers & Geosciences},
volume = {72},
pages = {84-93},
year = {2014},
issn = {0098-3004},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2014.07.005},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300414001629},
author = {Bernhard Bauer-Marschallinger and Daniel Sabel and Wolfgang Wagner},
keywords = {Remote sensing, High resolution, Big data, Global grid, Projection, Sampling, Equi7 Grid}
}



